Analysis of Contaminants by Thermal Desorption GC-MS
Home » Analysis of Contaminants by Thermal Desorption GC-MS
Thermal Desorption / Gas Chromatography / Mass Spectrometry combines the advantages of utilizing three techniques for solving difficult problems in organic analysis. Head Space Analysis (HSA), also known as Thermal Desorption, was initially developed for analysis of volatile compounds in matrices that could not be directly injected into a gas chromatograph. Dynamic Headspace is a non-equilibrium technique.
The technique works by subjecting the sample to elevated temperatures for a period of time to drive volatile compounds from the sample matrix into the atmosphere above the sample, called the “head space”. Helium continuously sweeps the chamber, carrying with it the components that have outgassed. The purge gas is passed through an adsorbent trap that contains (in order): glass beads, TenaxTM, and charcoal and is cooled down to -100°C. At the conclusion of the experiment, the trap is thermally desorbed (in reverse flow) directly into the inlet of a gas chromatograph. The components that were present on the trap are separated by Gas Chromatography and identified using Mass Spectrometry. An external standard usually deuterated n-hexadecane is used to provide semi-quantitative results.
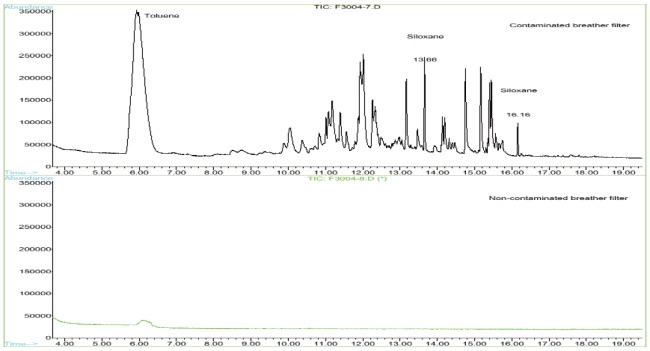
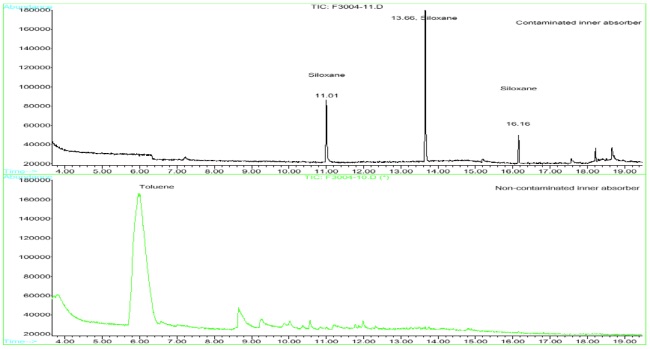
This short note presents a comparison of good and failed disk drives. The breather filters and internal absorbers were analyzed by Thermal Desorption GC/MS to identify contaminants that might be causing the failures. Figure 1 compares a siloxane (retention times of 13.66, 16.16 minutes) contaminated breather filter from a failed drive with a non-siloxane contaminated breather filter from a good drive. Figure 2 compares a siloxane (retention times 11.01, 13.66 and 16.16 minutes) contaminated inner absorber from the same failed drive with a non-siloxane contaminated inner absorber from the same good drive.
Thermal Desorption GC/MS analysis of this type is applicable to any type of sample, not just the disk drive filters used in this example. Any sample that fits in the thermal desorption chambers (1 1/2” diameter x 4” long) can be outgassed at any temperature between 45°C and 300°C, normally for a time period of one hour to three hours. Any volatile organic components will be detected and semi-quantitative results will be provided. Detection limits are as low as 10 ng/component.
Would you like to learn more about Analysis of Contaminants by GC-MS?
Contact us today for your analysis of contaminants by thermal desorption GC-MS needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.