Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
Home » Our Techniques » Mass Spectrometry » GC-MS
Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) combines two powerful techniques to provide the identification of compounds with low detection limits and the potential for quantitative analysis. Liquid, gaseous and solid samples work well with GC-MS analysis. However, analyzed compounds are typically volatile and semi-volatile.
In Gas Chromatography (GC), a sample is volatilized and carried by an inert gas through a coated glass capillary column. The “stationary phase” is bonded to the interior of the column. Retention time is how long that a compound takes to pass through the column to the detector. Finally, the sample is identified by comparing the sample with a reference.
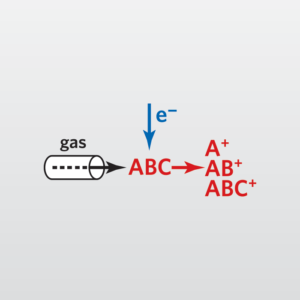
In the usual Mass Spectrometry (MS) step of GC-MS, compounds leaving the GC column are fragmented by electron impact. The charged fragments are detected, and the subsequent spectrum obtained can be used to identify the molecule. Fragmentation patterns are reproducible and can be used to produce quantitative measurements.
GC-MS analysis of liquids, gases and solids
Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry analyses are performed on liquids, gases or solids. For liquids and gases, the sample is commonly directly injected into the GC. For solids, the analysis is carried out by solvent extraction, outgassing (desorption) or pyrolysis.
Desorption experiments are performed under helium flow at a controlled temperature between 40-300 ºC, with analytes being collected on a cryogenic trap during desorption. The sample chamber is a 1.25”x4” cylinder.
Pyrolysis is another sampling technique for the analysis of materials that cannot be directly injected into the GC-MS. By applying heat directly to the sample, the molecule can be broken down in a reproducible way. After that, GC-MS analyzes smaller molecules that reach the GC. By this method, probe temperatures of up to 1400ºC can be used.
In addition, many other sample preparation and sampling methods are available — for example, derivatization, static headspace analysis, purge and trap, SPME (solid phase microextraction) — that have applications based on the sample type and species of interest.
Ideal Uses of GC-MS
- Identifying and quantifying volatile organic compounds in mixtures
- Outgassing studies
- Testing for residual solvents
- Identifying trace impurities in liquids or gases
- Evaluating extracts from plastics
- Evaluating contaminants on semiconductor wafers or other technology products (thermal desorption)
- Medical device chemical characterization via ISO 10993:18
Strengths
- Identification of organic components by separating complex mixtures
- Quantitative analysis
- Trace determination of organic contamination (low to mid-ppb level for liquid matrices and low nanogram level for solid matrices — Dynamic Headspace Analysis)
Limitations
- Firstly, target compounds must either be volatile or capable of derivatization
- Secondly, non-volatile matrices (wafers, oils, metal parts, etc.) require additional prep (extraction, outgassing, etc.)
- Thirdly, atmospheric gases are challenging (CO2, N2, O2, Ar, CO, H2O)
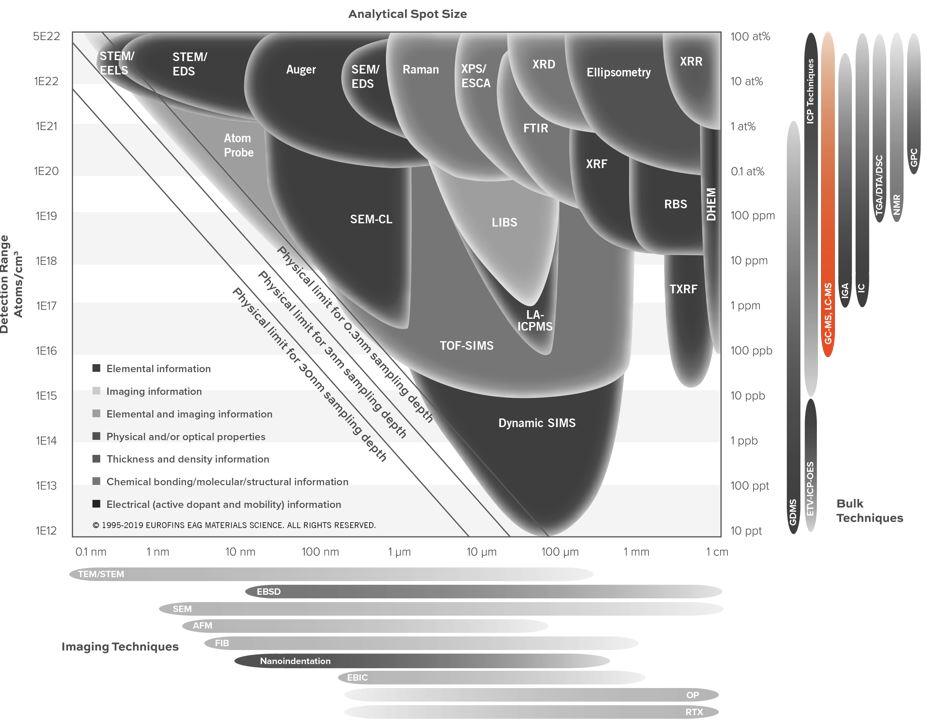
GC-MS Technical Specifications
- Signal Detected: Molecular ions and characteristic fragment ions
- Elements Detected: Molecular ions up to m/z 800
- Detection Limits: ~1 ng introduced to the column
Related Resources
Would you like to learn more about using GC-MS?
Contact us today for your GC-MS needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.