Hydrogen Forward Scattering Spectrometry (HFS)
Home » Our Techniques » Spectroscopy » HFS
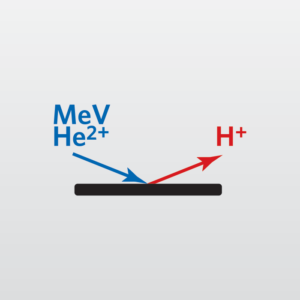
Hydrogen Forward Scattering Spectrometry (HFS) is an ion scattering technique that is used to quantitatively determine the vertical distribution of hydrogen in thin films. During the process, He2+ ions hit the sample surface at a glancing angle, knocking hydrogen atoms out of the sample, which can then be analyzed using a solid state detector.
The ability to measure the composition and vertical distribution of hydrogen content within a thin film can be critical due to the potential impact of hydrogen on a film’s physical or electrical properties. Other techniques, such as Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES), Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), cannot detect hydrogen; and while SIMS can measure hydrogen, quantification of the hydrogen by SIMS can be difficult and requires standards. This makes HFS a uniquely useful technique for thin film analysis.
Very few labs are able to offer HFS. EAG’s experience enables fast turnaround time, accurate data and person-to-person service, ensuring you understand what results mean for your materials and processes.
Ideal Uses of HFS
- Hydrogen analysis of thin films
Strengths
- Non-destructive H composition measurement
- Whole wafer analysis (up to 300 mm)
- Conductor and insulator analysis
Limitations
- Large analysis area (1×7 mm)
- Useful information limited to thin films (<0.4 μm)
- Depth resolution of 300 Å
Technical Specifications
- Signal Detected: Forward scattered H atoms
- Elements Detected: 1H, 2H
- Detection Limits: 0.1-0.5 at%
- Depth Resolution: ~300 Å
- Imaging/Mapping: No
- Lateral Resolution/Probe Size: ≥1×7 mm
Would you like to learn more about using Hydrogen Forward Scattering Spectrometry?
Contact us today for your Hydrogen Forward Scattering Spectrometry (HFS) needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.