Assessment of Nickel Exposure Risk of Intravascular Stents and Delivery Systems
Home » Assessment of Nickel Exposure Risk of Intravascular Stents and Delivery Systems
How do you evaluate nickel biocompatibility when developing innovative implantable materials?
How do you verify device safety after a process or material change? How do you develop the optimal testing strategy to evaluate nickel leaching? How do you investigate implant biocompatibility? ASK EAG. We Know How.
With an unparalleled suite of analytical instruments and over 35 years’ experience investigating material surface properties, EAG Laboratories offers medical device innovators a true R&D partnership. From evaluating pitting corrosion to characterizing surface oxides, no laboratory services company offers greater expertise in assessing the safety of nickel-containing implantable medical devices.
HOW WE CAN HELP
EAG brings multi-disciplinary analytical expertise and a deep understanding of materials to support the safety and effectiveness of implantable medical devices. Our scientists will recommend an optimal testing strategy to efficiently address FDA and other regulatory requirements and to help mitigate post-commercialization risk. Although nickel-rich materials provide excellent physical properties for the intended application, the risk of exposure to toxic nickel ions is a concern for patient safety.
The FDA has provided Guidance for testing intravascular stents for:
- Pitting corrosion potential
- Galvanic corrosion
- Surface characterization
- Nickel ion release
These implant devices are composed of materials made from nickel-rich alloys, including nitinol, stainless steel and MP35N.
Corrosion Testing
EAG scientists evaluate materials for both pitting corrosion and galvanic corrosion susceptibility using ASTM Standard Test Method F2129. As prescribed in the method, we assess small, metallic implantable medical devices and components using cyclic (forward and reverse) potentiodynamic polarization.
Surface Characterization
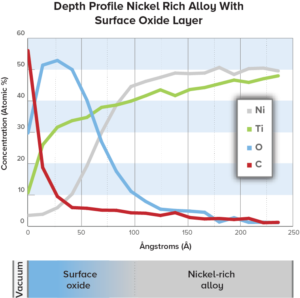
Due to the small lateral dimensions found on implantable devices, only a limited number of analytical techniques are capable of truly measuring surface composition or oxide thickness to the required specifications. EAG employs Auger Electron Spectroscopy to meet spatial resolution requirements and to address questions regarding oxide thicknesses, which are typically in the 20 – 200nm range for nitinol and similar materials.
Nickel Ion Release Testing
When stent materials fail to meet corrosion resistance and surface passivation criteria, regulators recommend nickel ion release testing to assess nickel biocompatibility. FDA guidance issued in August 2015 provides a standard protocol for in vitro nickel ion release testing. EAG scientists possess the technical expertise required to conduct a protocol-driven study to measure concentrations of nickel ions leached from a stent device under simulated conditions in a controlled environment, over a recommended testing period of at least 60 days. Normalized nickel ion release rates are an effective tool when comparing different nickel-rich, alloy-based devices. EAG has the expertise and capability to also analyze changes in the leached device itself, post test, as well as to determine the amount of Ni leached from the test sample into solution.
Failure Investigations
EAG scientists have years of experience investigating medical device failures, including fatigue resistance and hydrogen embrittlement. Metallographic examination of stents using optical or electron microscopy is a powerful tool for understanding the modes of medical device failures. EAG Laboratories has an unmatched ability to address all types of product failures, that may come to light at any stage of product development, including during testing.
From evaluating nickel biocompatibility per FDA August 2015 Guidance document, “Select Updates for Non-Clinical Engineering Tests and Recommended Labeling for Intravascular Stents and Associated Delivery Systems” to troubleshooting product failures, EAG Laboratories is your analytical partner. Many of our locations are ISO 17025-certified and/or FDA-registered.
Would you like to learn more about Nickel Exposure Risk of Intravascular Stents?
Contact us today for your nitinol or nickel-rich stent evaluations needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.