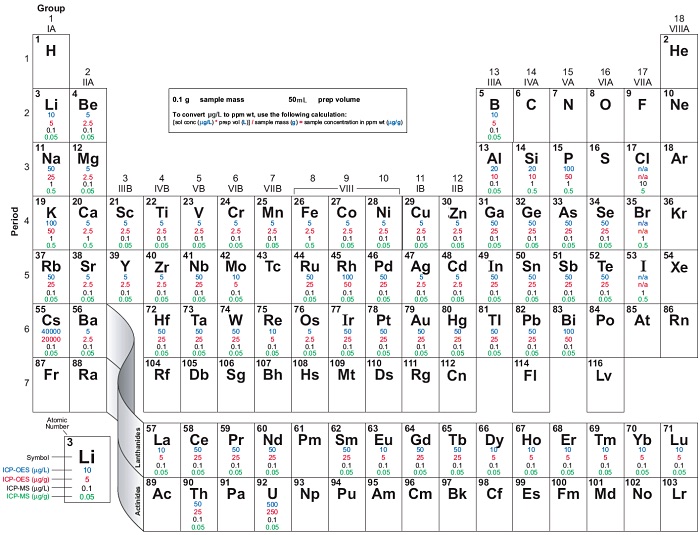
ICP-OES and ICP-MS Detection Limit Guidance
Home » ICP-OES and ICP-MS Detection Limit Guidance
These ICP-OES and ICP-MS detection limits are theoretical best case scenarios assuming there are no spectral interferences affecting the best isotope or wavelength for a given element. For any given determination, the actual method detection limit can be an order of magnitude higher or more. Use this as a guide, not absolute information.
Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) based analytical techniques can quantitatively measure bulk elemental composition of a material.
In plasma emission spectroscopy (OES), a sample solution is introduced into the core of an inductively coupled argon plasma (ICP), which generates temperatures on the order of 9,000K. At these temperatures, analyte atoms and ions become thermally excited and emit light at their characteristic wavelengths. This light
is focused on to the entrance slit of the spectrometer and passes through a diffraction grating that resolves the light into a spectrum of its constituent wavelengths. Within the spectrometer, this diffracted light is then separated and collected by wavelength and amplified to yield an intensity measurement that can be converted to an elemental concentration by comparison with calibration standards.
In plasma mass spectrometry (MS), the inductively coupled argon plasma (ICP) is once again the high temperature source and is coupled to a quadrupole mass analyzer. However in contrast to OES, the plasma in ICP-MS is used to generate ions that are accelerated into a quadrupole mass analyzer. The ions are then separated and collected according to their mass to charge ratios. The constituents of an unknown sample can then be identified and measured. ICP-MS offers extremely high sensitivity to a wide range of elements.
Strengths
- Bulk chemical analysis technique that can determine simultaneously up to 70 elements in a single sample analysis.
- The linear dynamic range is over several orders of magnitude.
- Instrumentation is suitable to automation, thus enhancing accuracy, precision and throughput.
Limitations
- The emission spectra are complex and inter-element interferences are possible if the wavelength of the element of interest is very close to that of another element.
- In mass spectrometry, determination and quantification of certain elements can be affected by interference from polyatomic species, matrix elements and atmospheric elements.
- The sample to be analyzed must be completely digested, or dissolved prior to analysis in order to determine the element(s) of interest.
Would you like to learn more about ICP-OES and ICP-MS Detection Limits?
Contact us today for your ICP-OES and ICP-MS needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.