Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) Services
Home » Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) Services
Eurofins EAG Laboratories (EAG) offers comprehensive compositional analysis services, including “full scan” measurements of up to 69 elements, through its suite of Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) Analytical Techniques.
Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) comprises a family of widely used instrumental analytical
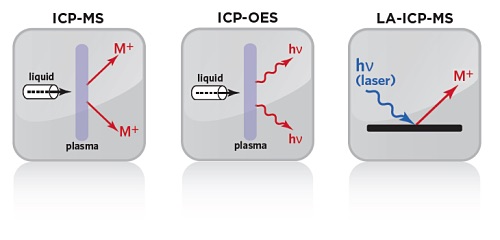
chemistry techniques spanning both atomic spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. EAG offers Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES), Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS), and Laser Ablation-Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). This diverse array of techniques is unified by its common method of sample ionization: the Inductively Coupled Plasma.
ICP-OES VS ICP-MS: A COMPARISON OF THE TWO TECHNIQUES
ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry) measures the light emitted at element-specific characteristic wavelengths from analytes. A detector measures the intensity of the emitted light, which is then used to evaluate the concentration of that particular element in the sample by comparison with calibration standards.
ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry) measures the intensity of analyte ions generated in the inductively coupled plasma source. The ions created in the plasma are separated by their mass to charge ratios, enabling the identification and quantitation of the analytes present. ICP-MS offers superior sensitivity (i.e. low detection limits) for a wide range of elements.
LASER ABLATION INDUCTIVELY COUPLED PLASMA MASS SPECTROMETRY (LA-ICP-MS)
In Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry, the sample is directly analyzed by ablating a solid sample with a pulsed laser beam. The created aerosols are transported by a gas stream into the core of inductively coupled argon plasma (ICP). The plasma in ICP-MS is used to generate ions that are then introduced to the mass analyzer. The constituents of an unknown sample can then be identified and measured.
For laser ablation, any type of solid sample can be ablated for analysis; there are few sample-size restrictions and no sample preparation procedures. Chemical analysis using laser ablation requires a smaller amount of sample (micrograms) than that required for solution ICP-MS (milligrams). Depending on the analytical measurement system, very small amounts of sample may be sufficient for this technique. In addition, a focused laser beam permits spatial characterization of heterogeneity in solid samples, with typically micron resolution both in terms of lateral (x, y) and depth (z) directions.
Would you like to learn more about Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) Services?
Contact us today for your Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.