Quantitative Determination of Nonylphenol Ethoxylates
Home » Quantitative Determination of Nonylphenol Ethoxylates
This method is for the quantitative determination of nonylphenols and nonylphenol ethoxylate (NPEs) by LC-MS.
NP/NPEs, also known as nonylphenols and nonylphenol ethoxylates, are nonionic surfactants, or detergent-like substances, with uses that lead to widespread release into aquatic environments. NPEs are used as detergents, emulsifiers, wetting agents, industrial processes, personal hygiene, automotive, latex paints, and lawn care products. Their presence in the environment is solely due to human activities, and mainly from WWTPs (waste water treatment plant) and direct discharge. Over 80% of alkylphenol produced are nonylphenol based compounds. The rest are mostly octylphenol based compounds.
NPEs are degraded to shorter chain nonylphenol ethoxylates as well as shorter nonylphenol ethoxycarboxylates under aerobic condition, before being biodegraded to nonylphenol. Shorter ethoxylate chain NPEs have greater toxicity than longer ones. These shorter chain NPEs have been reported to cause a number of estrogenic responses on aquatic organisms and thus they have been classified as endocrine disruptors (EDCs) by several organizations2. We have developed a method using liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry for identification and quantitation of NPEs.
Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
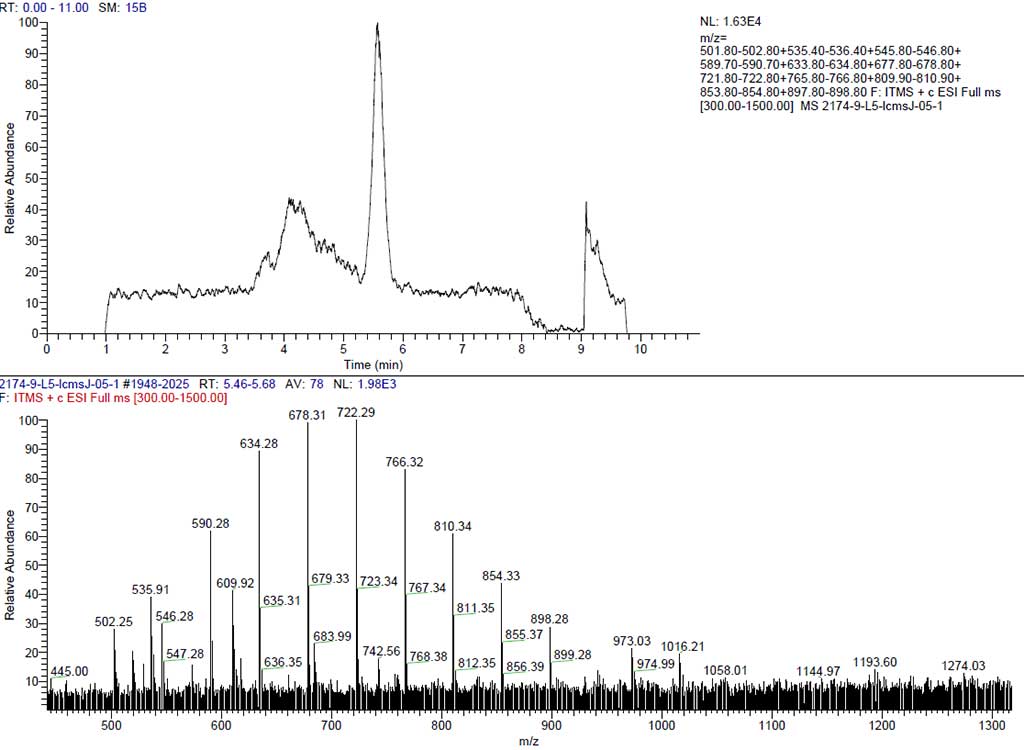
LC/MS is on the STL 17025 Scopes of Accreditation. LC-MS combines the techniques of HPLC and MS to characterize the structures of components in a complex matrix. HPLC is used for the separation of the compounds in the sample. A mixture of solvents or solutions, called the mobile phase, is forced at high pressure through a packed column, usually of coated silica particles, called the stationary phase. Components in the mixture are separated based on the difference in their affinities for the stationary phase and the mobile phase and can be detected and measured as they elute from the column. Typically, HPLC detection is performed using a UV detector monitoring absorption at a target wavelength or wavelengths. The time a chemical component spends in the column from injection until detection is known as retention time and is an indicator of component identity when compared with the retention time of known standards under the same conditions. The measured peak area or height is concentration dependent and may be used to quantify the component. Figure 1 shows the chromatographic and mass spectra profile of the standard.
Would you like to learn more about Determination of Nonylphenol Ethoxylates?
Contact us today for your determination of Nonylphenol Ethoxylate needs. Please complete the form below to have an EAG expert contact you.