
EAG’s Expertise in Supporting the Aviation Industry
EAG provides a number of services to ensure the safety in manufacturing and performance for the aviation industry.
Home » Principles and Strengths of In Vitro Testing
In vitro is the Latin term for “in glass,” meaning that the testing is performed in a container that is outside of a living organism. This testing uses cell-based biological models instead of animals or humans. In vitro efforts help fulfil the FDA’s “3Rs approach” to replace, reduce, and/or refine animal testing.
Replace
Reduce
Refine
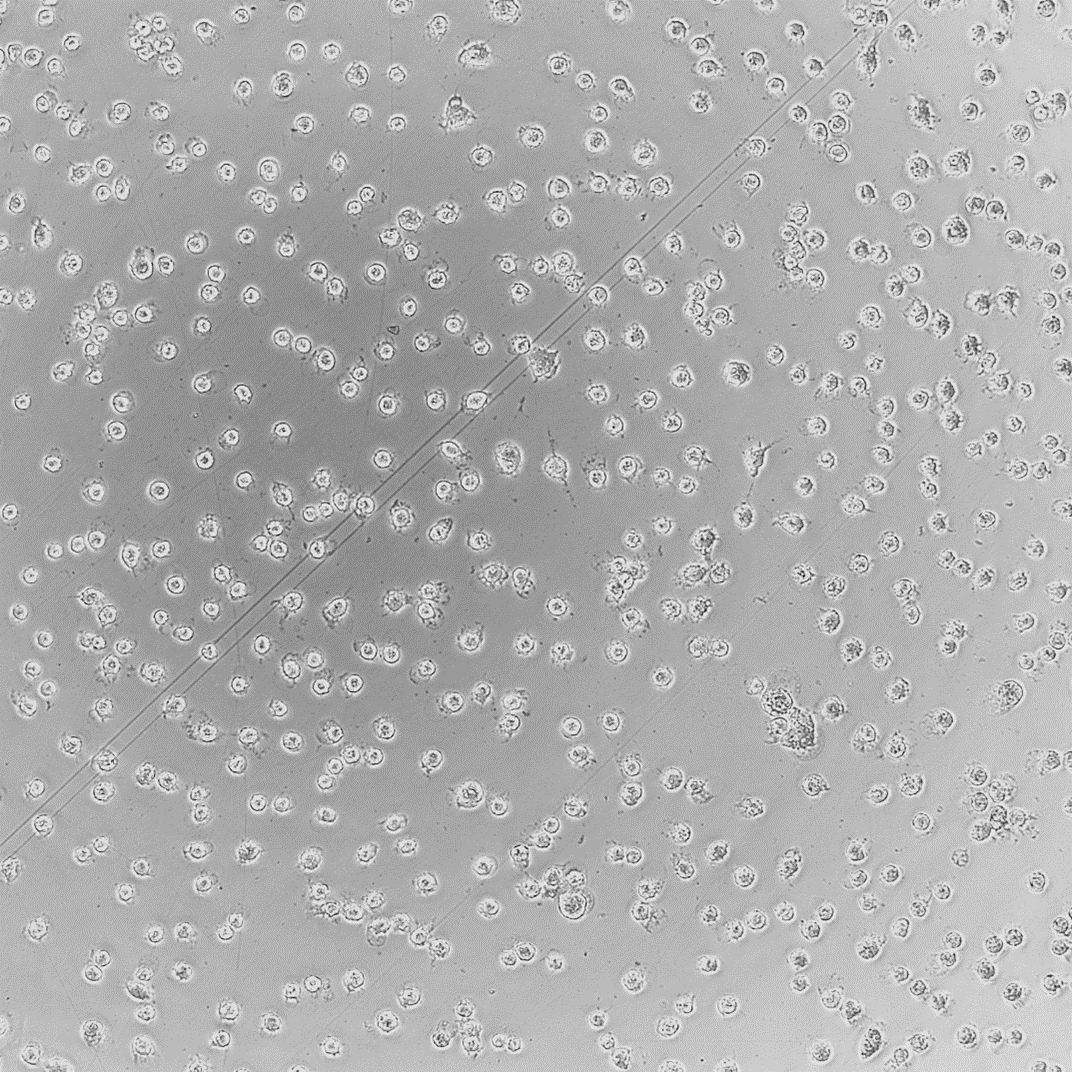
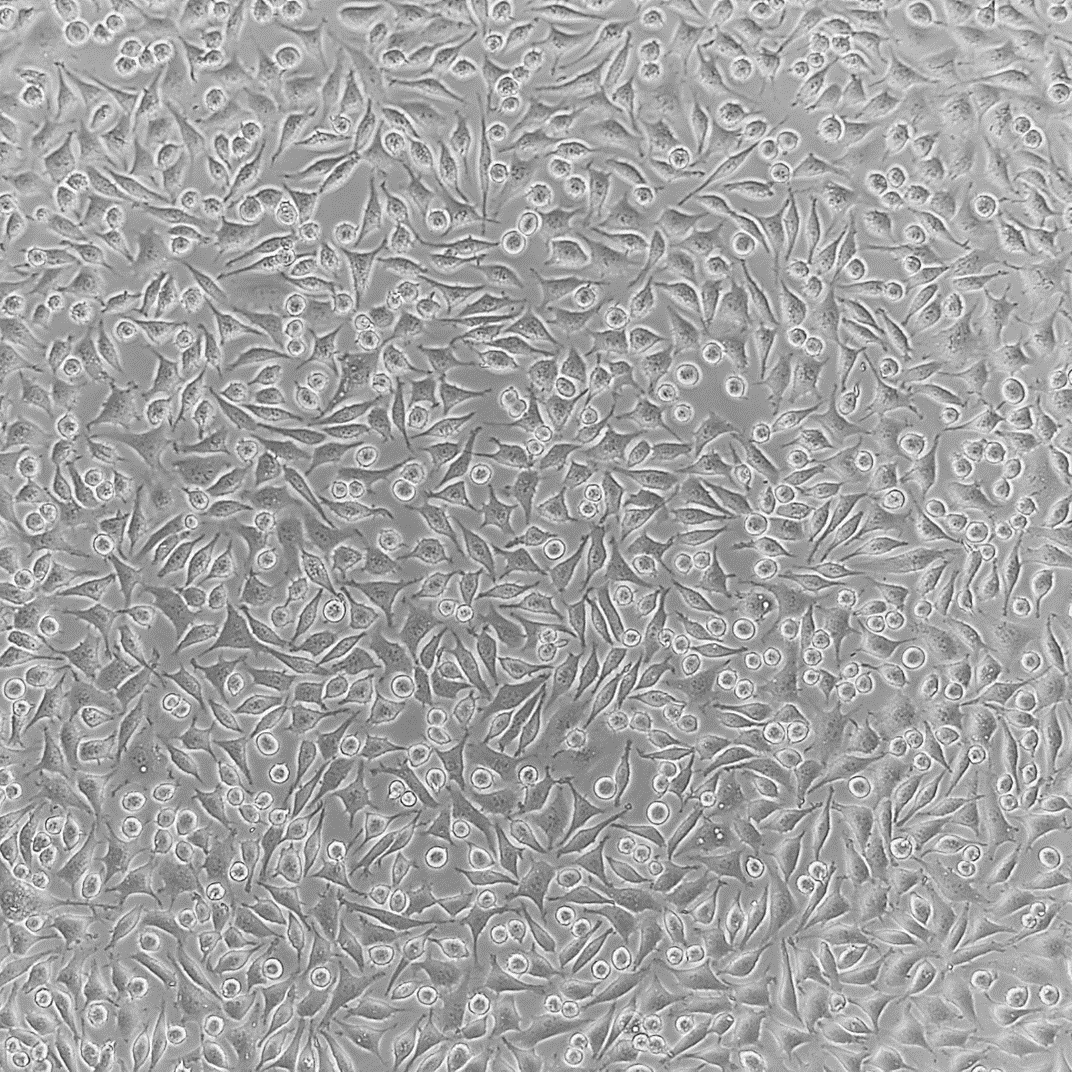
In Vitro model systems can be specified to the test sample’s intended use. 2D cell cultures are grown rapidly for high-throughput or multi-sample analysis with minimized variation between treatments. Cell cultures can also be made into 3D tissue models. These models contain differentiated cell layers to physiologically represent complex tissues and evaluate specific endpoints. Using specific geometries, in vitro cell culture models can be used to evaluate simple and complex biological responses.
To assess different biological endpoints, various forms of analytical methods may be implemented. Measurable responses of the in vitro models include cell death, growth inhibition, genetic alterations, changes in surface marker expression and altered metabolism.

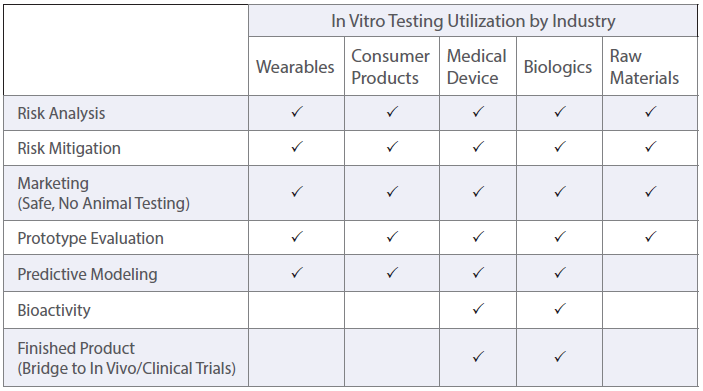

EAG provides a number of services to ensure the safety in manufacturing and performance for the aviation industry.

FIB Circuit Edit provides the ability to quickly perform nano-surgury by cutting traces or adding metal connections at the chip level

Our laboratories in France and the Netherlands offer materials testing for industries including semiconductor, consumer electronics, lighting, aerospace and healthcare.

A device manufacturer observed defects in a lot of thermoplastic tubing. The tubing exhibited signs chemical attack or exposure to heating.
To enable certain features and improve your experience with us, this site stores cookies on your computer. Please click Continue to provide your authorization and permanently remove this message.
To find out more, please see our privacy policy.