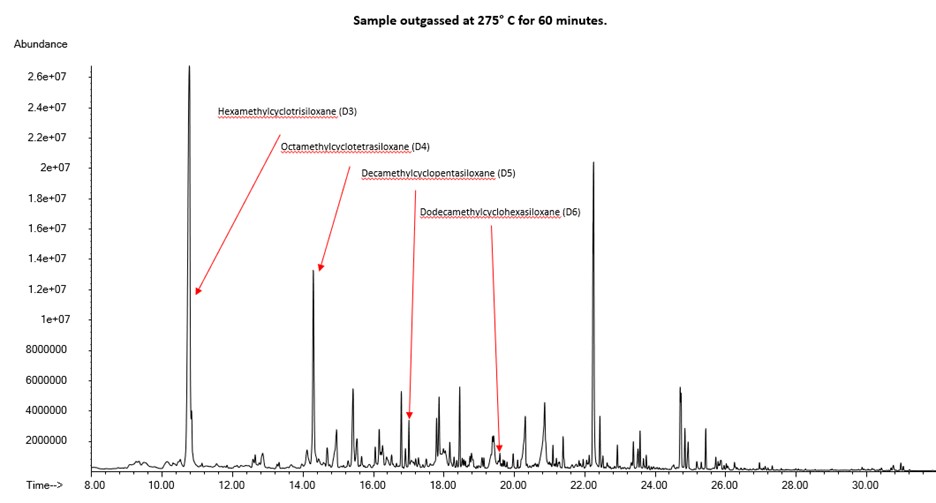
Using MicroXRD to Identify the Composition of Sand
XRD analysis can be used on many scientific and technology-based applications where you may want to identify the crystalline material in a very small area or volume, such as glass defects or inclusions, integrated circuits, LEDs and more.